To start with fill the details given at the top of the form.
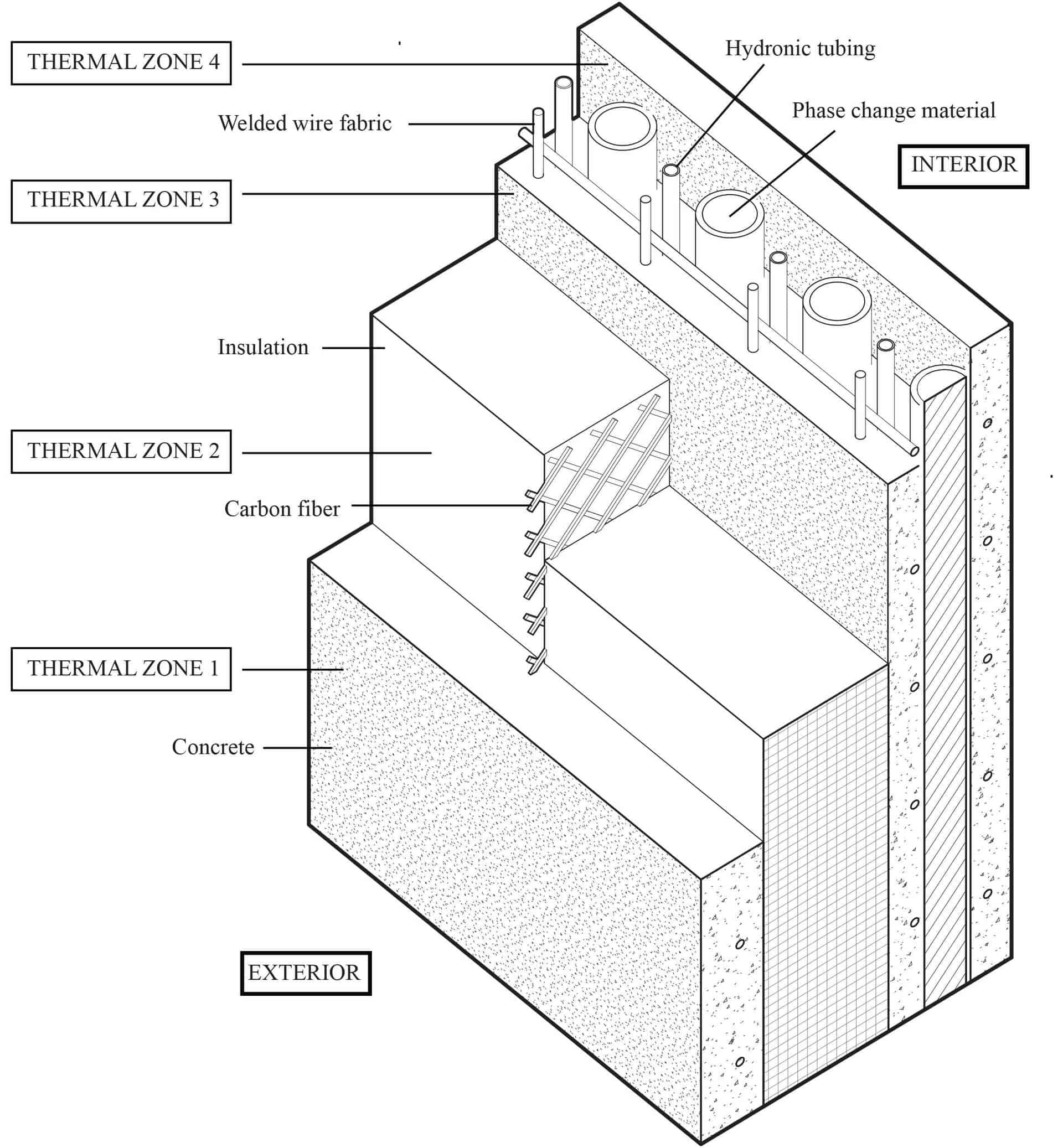
Sensible heat load in for concrete walls.
Ashrae tables are for latitude 24 o n 36 o n or 48 o n which cover u.
These are given below.
An account of the total heat flow into or out of a home depending on the time of year.
Other sensible heat gains are taken care of by the hvac equipment before the air reaches the rooms system gains.
Wall or roof type.
C added into the calculations simply because it is a valuable resource for heating.
This simple calculation is based on a rule of thumb that the specific heat of most concretes is very close to 0 21 btu lb ºf 880 j kg k.
Clf cooling load factor 2 2 heat gain due to human beings the human body in a cooled space involved cooling load of sensible and latent heat.
Notice that below grade walls below grade floors and floors on concrete slabs do not increase the cooling load on the structure and are therefore ignored.
Now that we have seen the various heat loads inside the room and also surveyed the room let us see one example heat load calculations for the residential building using the heat load calculations form shown below.
East wall q 8x35 2 2 5x4 95 80 26 150 btu hr.
B neglected when doing heating load calculations because they are not dependable heat sources.
Such as a heat pump to upgrade the temperature level to satisfy the required heat load which also incurs higher investment cost.
Q sensible heat gain through wall or roof.
Using equation 5 the thermal resistance of the 4 inch concrete wall with 2 inch insulation is r 1 6 1 0 2 17 4 10 2 17 45 1 1 63 26 hr ft 2 f btu equation 2 gives the heat conducted through the wall area minus the window area assuming 8 foot high walls.
The heat gain from occupants is based on the average.
Therefore for example a single wythe concrete masonry wall weighing 34 lb ft 166 kg m has a.
Wall or roof exposure orientation.
Cltd cooling load temperature difference from ashrae table for a given.
In an air conditioned room sensible heat load and it all happened due to temperature different between body and room air.
A systematic method of evaluation to estimate heat loss sensible and latent heat gain.
A added into the calculations because it is a large volume of energy and extremely valuable in reducing the total heating load.
A surface area of wall or roof.
Example heat load calculations.
We need to do load calculations in order choose equipment that will make an occupant comfortable and safe and to keep energy costs down.
Sensible heat gain is directly added to the conditioned space by conduction convection and or radiation.
View chapter purchase book.